Table of Contents
Overview – The Endocrine Examination
The endocrine examination is a structured clinical assessment designed to detect systemic manifestations of hormonal disorders, including diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, adrenal dysfunction, pituitary pathology, and metabolic syndromes. The endocrine examination involves close inspection for subtle changes in facies, body habitus, skin, and neuromuscular status. It is a high-yield exam often featured in OSCEs and inpatient assessments due to the diverse and recognisable constellation of signs across the body.
Definition
The endocrine examination is a systemic physical assessment focused on identifying characteristic signs of hormonal imbalances and endocrine pathology. It involves observation, palpation, and neurological assessment to detect common disorders such as Cushing’s syndrome, hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, and polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS).
General Inspection
Facies
- Moon facies → Cushing’s syndrome
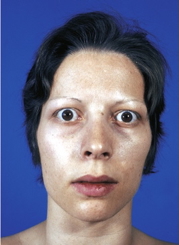
- Frightened stare, lid lag, exophthalmos → Graves’ disease (hyperthyroidism)
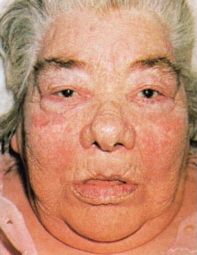
- Puffy face, anhedonic expression, myxoedema → Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (hypothyroidism)
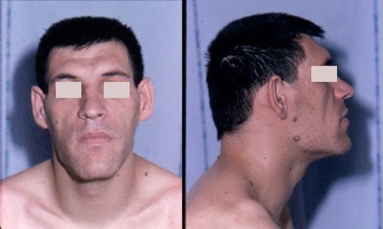
- Frontal bossing, large jaw/tongue/nose/ears → Acromegaly
- Hyperpigmented, thin appearance → Addison’s disease
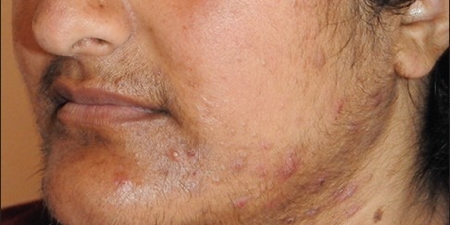
- Hirsutism and male-pattern balding → PCOS

Body Habitus
- Obesity → Type 2 diabetes mellitus, Cushing’s, hypothyroidism
- Wasting → Type 1 diabetes mellitus, Addison’s, hyperthyroidism
- Central adiposity → Cushing’s syndrome
Hair and Pigmentation
- Hair loss → Hypothyroidism
- Hirsutism → Cushing’s, PCOS
- Generalised hyperpigmentation → Addison’s disease, haemochromatosis
- Acanthosis nigricans → Diabetes, Cushing’s, acromegaly, PCOS
Mental State
- Bradyphrenia, slow responses, low affect → Hypothyroidism, Addison’s, DKA, HONC
Vital Signs
- Pulse:
- Tachycardia → Hyperthyroidism, phaeochromocytoma, diabetic ketoacidosis
- Bradycardia → Hypothyroidism
- Blood Pressure:
- Hypertension → Seen in hypo-/hyperthyroidism, Cushing’s, Conn’s, phaeochromocytoma, PCOS, acromegaly
- Hypotension → Addison’s disease
- Respiratory Rate:
- Tachypnoea → Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Temperature:
- Hyperthermia → Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothermia → Hypothyroidism
Hands
- Warm, erythematous, moist → Hyperthyroidism, phaeochromocytoma, acromegaly
- Cold, dry, pale → Hypothyroidism
- Tremor → Hyperthyroidism, phaeochromocytoma
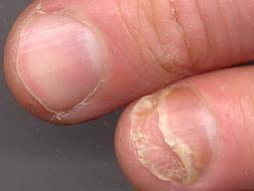
- Clubbing, thyroid acropachy, Plummer’s nails → Graves’ disease
- Brittle nails → Hypothyroidism
- Palmar crease pigmentation → Addison’s disease
- Spade-like hands, osteoarthritic changes → Acromegaly
- Xanthomata → Dyslipidaemia in hypothyroidism, diabetes, PCOS, Cushing’s, acromegaly
Arms
- Proximal myopathy → Common in hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, Cushing’s, acromegaly
- Hyperreflexia → Hyperthyroidism
- Delayed (“hung”) reflexes → Hypothyroidism
- Muscle wasting → Diabetes, Addison’s
Face
- Pallor, cyanosis, conjunctival or buccal changes
- Loss of lateral eyebrow, receding hairline, periorbital myxoedema → Hypothyroidism
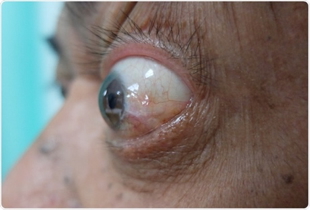
- Exophthalmos, lid lag → Hyperthyroidism
- Xanthelasma → Hyperlipidaemia
- Visual field loss → Pituitary tumour (bitemporal hemianopia)
- Fundoscopy → Diabetic or hypertensive retinopathy
- Mouth:
- Buccal pigmentation → Addison’s
- Infections → Diabetes, Cushing’s
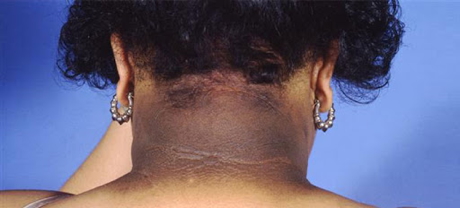
Neck
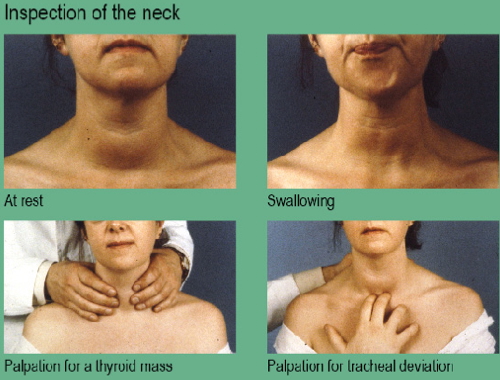
- Thyroid Examination:
- Inspect for scars (thyroidectomy), goitre
- Palpate thyroid from behind: size, tenderness, consistency, mobility
- Listen for thyroid bruits → Hyperthyroidism
- Assess for cervical lymphadenopathy → Graves’, Hashimoto’s
- Retrosternal extension: Pemberton’s sign, raised JVP, percussion dullness
- Other Neck Signs:
- Acanthosis nigricans (posterior neck)
- Buffalo hump, supraclavicular fat pads → Cushing’s
- Carotid bruits → Diabetes, acromegaly, PCOS

Chest
- Hair distribution → PCOS
- Gynaecomastia → Hyperthyroidism, acromegaly, Cushing’s
- Skeletal signs:
- Bone tenderness → Osteoporosis (Cushing’s), hyperparathyroidism, acromegaly
- Cardiac signs:
- Displaced apex/murmurs → Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in acromegaly
- Effusions → Hypothyroidism
- Skin: Molluscum fibrosum in axilla (acromegaly)

Abdomen
- Central adiposity → Diabetes, Cushing’s
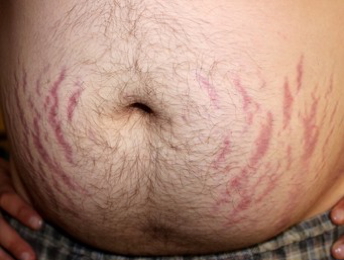
- Striae (purple, wide) → Cushing’s
- Injection site lipoatrophy → Diabetes
- Hepatomegaly → Fatty liver (diabetes, PCOS), GH excess (acromegaly)
- Splenomegaly and renal enlargement → Acromegaly
- Adrenal masses → Cushing’s, Conn’s, Addison’s, phaeochromocytoma
- Ovarian masses → PCOS
- Bowel sounds:
- Hyperactive → Hyperthyroidism
- Hypoactive → Hypothyroidism
Legs
- Proximal myopathy
- Quadriceps wasting → Diabetic amyotrophy
- Injection site lipoatrophy
- Pretibial myxoedema → Hyperthyroidism
- Non-pitting oedema → Hypothyroidism
- PVD signs → Shiny skin, hair loss, pitting oedema
- Charcot’s joint → Diabetes
- Ulcers:
- Arterial or venous in diabetes
- Neurological signs:
- Hyperreflexia → Hyperthyroidism
- Hung reflexes → Hypothyroidism
- Foot drop → Acromegaly (peroneal nerve entrapment)

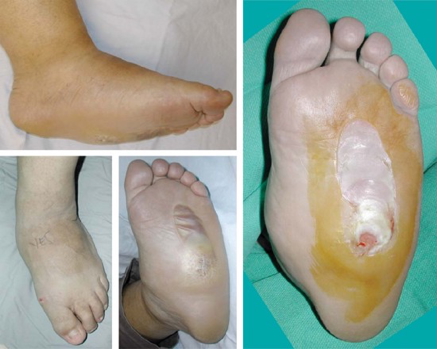
Feet
- Tendon xanthomata
- Warm, erythematous, well-perfused feet → Hyperthyroidism
- Cold, dry, poorly perfused → Hypothyroidism
Diabetic Leg & Foot Exam
General Inspection:
- Quadriceps wasting
- PVD signs: shiny skin, pitting oedema, ulcers
- Neuropathic changes: Charcot’s joint, necrobiosis lipoidica
- Xanthomata
- Deformities: bunions, hammer toes, pes cavus, hallux valgus
- Fungal nail infections
Neurological Testing (with eyes closed):
- Light touch: Monofilament on toes and dermatomes
- Vibration: Tuning fork – start distally
- Proprioception
- Pain: Pin-prick all dermatomes
- Power: Muscle strength
- Reflexes
Summary – The Endocrine Examination
The endocrine examination provides a comprehensive assessment of multisystem signs related to hormonal imbalance, including features of diabetes, thyroid disease, adrenal insufficiency, and pituitary dysfunction. Mastery of this exam enables early identification of serious endocrine pathology and is an essential OSCE skill. For a broader context, see our Clinical Skills Overview page.