Table of Contents
Overview – Lower Limb Innervation
Lower limb innervation arises primarily from the lumbar and sacral plexuses, which together coordinate motor and sensory supply to the pelvis, thigh, leg, and foot. These complex neural pathways are vital for movement, reflexes, and sensation. Understanding their anatomy is essential for identifying the effects of injuries, nerve compression, or systemic neuropathies affecting the lower extremity.
Definition
Lower limb innervation refers to the network of spinal nerves (from T12–S4) forming the lumbar and sacral plexuses, which give rise to peripheral nerves supplying all motor and sensory functions of the lower limbs and pelvic girdle.
Lumbar Plexus (T12–L4)
| Nerve | Root Origin | Course & Targets |
|---|---|---|
| Femoral | L2–L4 | Between Psoas major & Iliacus → under inguinal ligament → anterior thigh |
| Obturator | L2–L4 | Medial to Psoas → through obturator canal → medial thigh |
| Lateral Femoral Cutaneous | L2–L3 | Runs laterally across iliacus to ASIS → lateral thigh (sensory only) |
| Genitofemoral | L1–L2 | Through Psoas → divides into genital & femoral branches |
| Iliohypogastric & Ilioinguinal | L1 | Run across quadratus lumborum → lower abdominal wall |
| Lumbosacral Trunk | L4–L5 | Joins sacral plexus; important for communication between lumbar and sacral roots |




2. Gray822_es.svg: *Gray822.png: Grayderivative work: Ninovolador (talk)derivative work: Mcstrother, CC BY 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
Femoral Nerve
- Branches off: L2–L4
- Divisions:
- Anterior division: Pectineus, Sartorius + cutaneous branches
- Posterior division: Quadriceps femoris + saphenous nerve (cutaneous)
- Motor Innervation:
- Pectineus
- Sartorius
- Quadriceps: Rectus femoris, Vastus medialis/intermedius/lateralis
- Sensory Innervation:
- Anteromedial thigh
- Medial lower leg and foot (via saphenous nerve)


Obturator Nerve
- Branches off: L2–L4
- Course: Medial to Psoas → through obturator canal
- Motor Innervation:
- External obturator
- Adductor longus, brevis, magnus (part)
- Gracilis
- Sensory Innervation:
- Medial thigh


Sacral Plexus (L4–S4)
| Nerve | Root Origin | Innervates |
|---|---|---|
| Superior Gluteal | L4–S1 | Gluteus medius & minimus, Tensor fasciae latae |
| Inferior Gluteal | L5–S2 | Gluteus maximus |
| Sciatic Nerve | L4–S3 | Hamstrings, part of adductor magnus; splits into Tibial & Common Fibular |
| Tibial Nerve | L4–S3 (via sciatic) | Posterior leg + foot (motor & sensory) |
| Common Fibular | L4–S2 (via sciatic) | Anterior/lateral leg + dorsum of foot (motor & sensory) |
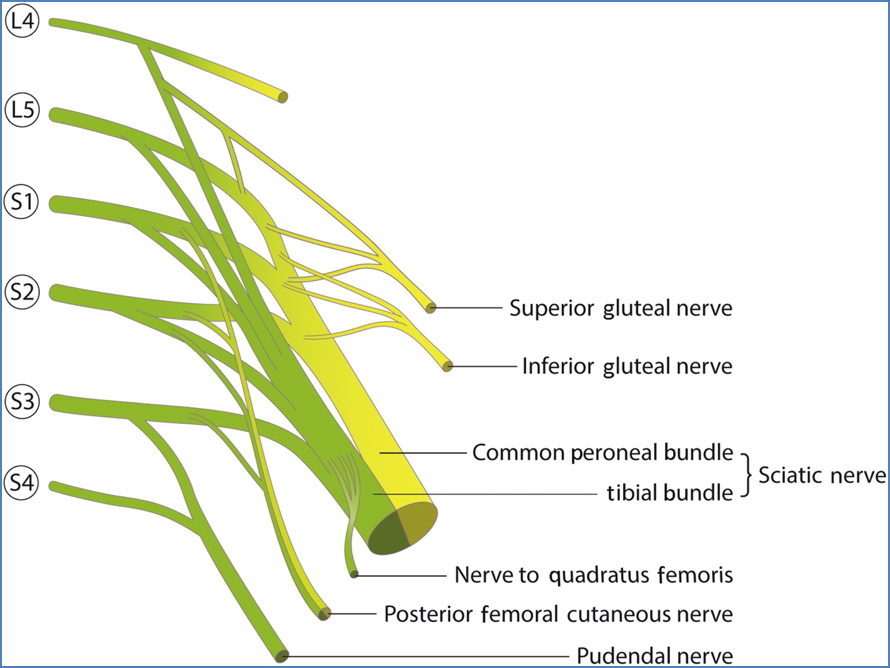
Superior Gluteal Nerve
- Branches off: L4, L5, S1
- Exits pelvis: Greater sciatic foramen (above piriformis)
- Motor Innervation:
- Gluteus medius
- Gluteus minimus
- Tensor fasciae latae
Inferior Gluteal Nerve
- Branches off: L5, S1, S2
- Exits pelvis: Greater sciatic foramen (below piriformis)
- Motor Innervation:
- Gluteus maximus
Sciatic Nerve
- Branches off: L4–S3
- Course: Exits pelvis through greater sciatic foramen → descends posterior thigh → bifurcates into Tibial and Common Fibular nerves
- Motor Innervation:
- Hamstrings (except short head of biceps femoris)
- ½ of adductor magnus

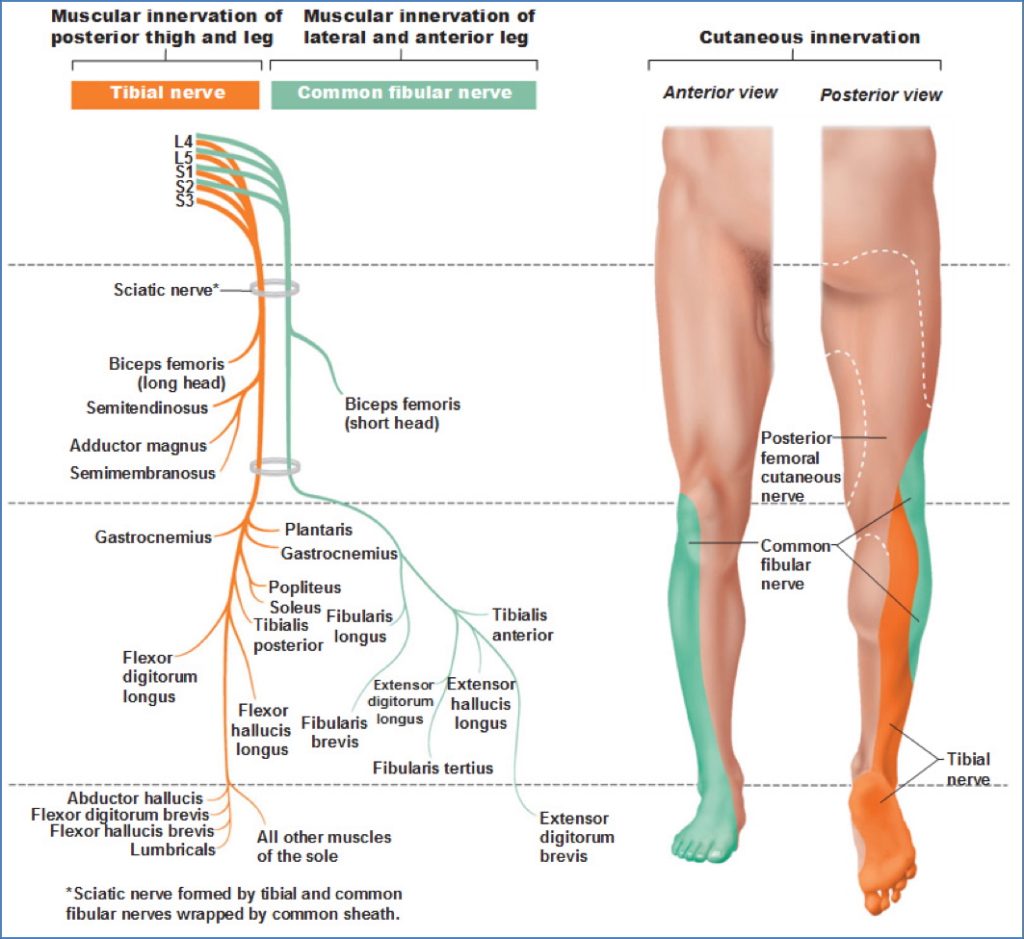
Tibial Nerve
- Course: Through popliteal fossa → posterior leg → behind medial malleolus → plantar foot
- Motor Innervation:
- Gastrocnemius
- Soleus
- Plantaris
- Tibialis posterior
- Flexor digitorum longus
- Flexor hallucis longus
- Branches into: Medial & lateral plantar nerves (foot intrinsic muscles)
Common Fibular (Peroneal) Nerve
- Course: Lateral popliteal fossa → winds around fibular neck → divides
- Divisions:
- Deep Fibular Nerve:
- Tibialis anterior
- Extensor digitorum longus
- Fibularis tertius
- Extensor hallucis longus
- Superficial Fibular Nerve:
- Fibularis longus
- Fibularis brevis
- Deep Fibular Nerve:
- Sensory Innervation:
- Lateral leg (superficial)
- Dorsum of foot
- First webspace (deep)

Common Lower Limb Nerve Lesions
| Nerve Affected | Functional Loss |
|---|---|
| Femoral | Weak hip flexion, loss of knee extension |
| Obturator | Weak hip adduction, altered gait |
| Tibial | Loss of plantar flexion, toe movement |
| Deep Fibular | Foot drop, loss of toe extension |
| Superficial Fibular | Loss of foot eversion |
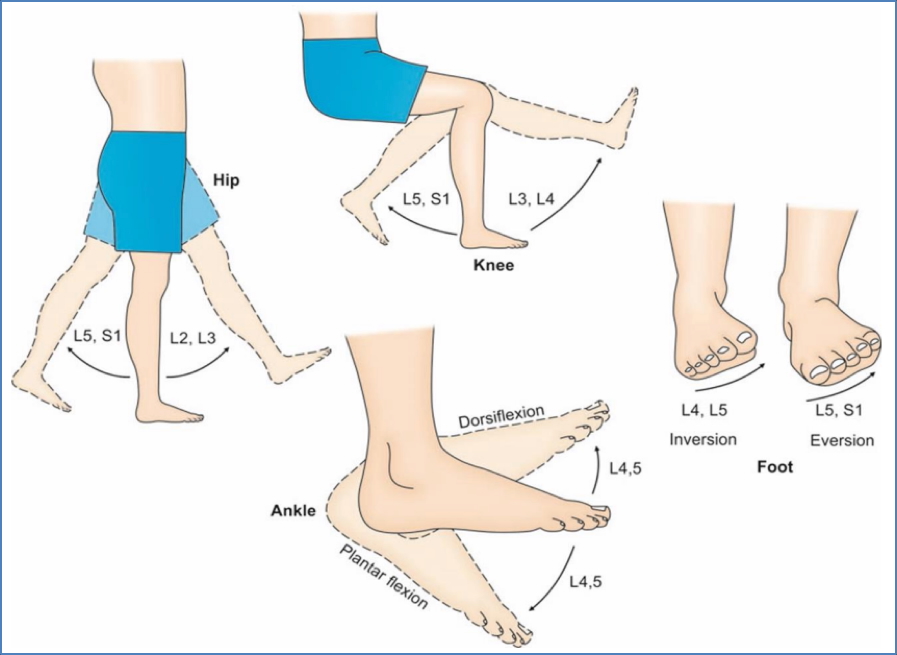

Most nerve lesions in the lower limb are incomplete, but can significantly impair mobility.
Summary – Lower Limb Innervation
Lower limb innervation is coordinated by the lumbar and sacral plexuses. The femoral and obturator nerves serve the anterior and medial thigh, while the gluteal and sciatic branches control posterior and distal lower limb function. Tibial and fibular nerves further divide to innervate the foot. Knowledge of this network is essential for understanding lower limb deficits. For a broader context, see our Musculoskeletal Overview page.