Table of Contents
Overview – Lower Limb Muscles
The lower limb muscles play a crucial role in locomotion, posture, and dynamic stability. These muscles are compartmentalised by function and innervation and are essential to understand in clinical assessments of gait, nerve injuries, and musculoskeletal pathology. This article presents a high-yield summary of the origins, insertions, actions, and nerve supply of major lower limb muscles, from the pelvis to the foot.
Definition
Lower limb muscles refer to all skeletal muscles arising from the pelvis and extending through the thigh, leg, and foot. They are systematically organised into functional compartments and are vital for standing, walking, and running.
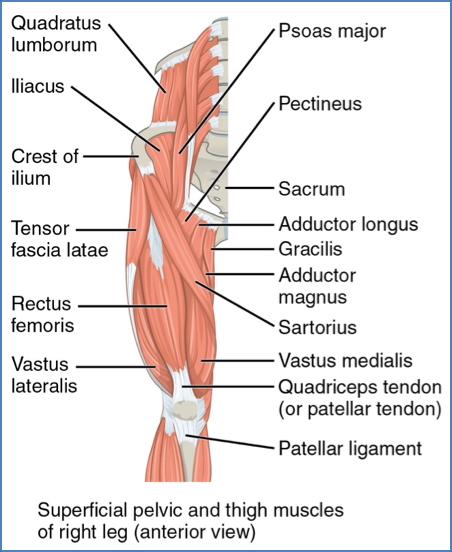
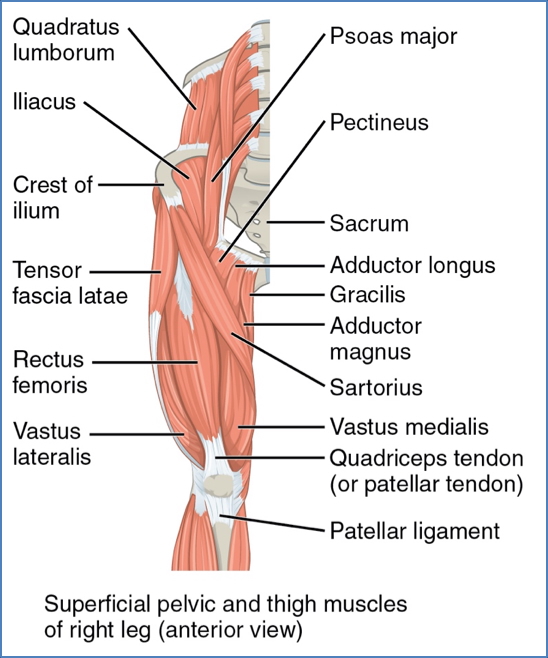
Muscles Originating on the Pelvis
| Muscle | Nerve Supply | Origin → Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sartorius | Femoral Nerve | ASIS → Medial aspect of proximal tibia | Hip flexion, abduction, lateral rotation; weak knee flexion |
| Iliacus | Femoral Nerve | Iliac fossa/crest, lateral sacrum → Lesser trochanter (via iliopsoas tendon) | Flexes thigh (e.g., bowing motion) |
| Psoas Major | L1–L3 Ventral Rami | Lumbar vertebrae (TPs, bodies, discs) → Lesser trochanter (via iliopsoas tendon) | Lateral flexion of vertebral column; postural stabiliser |

Thigh Muscles – Medial Compartment
| Muscle | Nerve Supply | Origin → Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
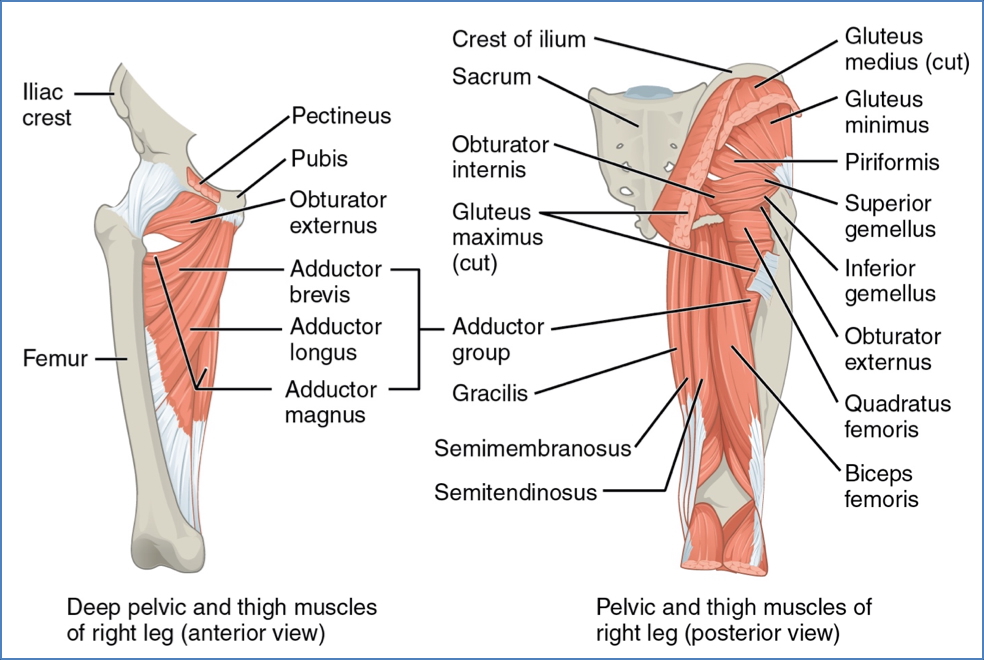
| Gracilis | Obturator Nerve | Inferior pubic ramus → Medial tibia (below condyle) | Adducts, flexes, medially rotates thigh; flexes knee |
| Pectineus | Femoral Nerve | Pubic crest → Posterior femur (between LT & linea aspera) | Adducts, flexes, medially rotates thigh |
| Adductor Brevis | Obturator Nerve | Inferior pubic ramus → Linea aspera (above longus) | Adducts, medially rotates thigh |
| Adductor Longus | Obturator (anterior) | Pubis near symphysis → Linea aspera | Adducts, flexes, medially rotates thigh |
| Adductor Magnus | Obturator & Sciatic | Ischial & pubic rami + ischial tuberosity → Linea aspera & adductor tubercle | Ant: adducts, flexes, medially rotates; Post: extends thigh |


Thigh Muscles – Anterior Compartment
| Muscle | Nerve Supply | Origin → Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensor Fasciae Latae | Sup. Gluteal Nerve | ASIS → Iliotibial tract | Flexes, abducts, medially rotates thigh |
| Rectus Femoris | Femoral Nerve | AIIS & acetabular rim → Patella & tibial tuberosity | Flexes thigh, extends knee |
| Vastus Lateralis | Femoral Nerve | Greater trochanter → Patella & tibial tuberosity | Extends and stabilises knee |
| Vastus Medialis | Femoral Nerve | Linea aspera & intertrochanteric line → Patella | Extends knee; inferior fibres stabilize patella |
| Vastus Intermedius | Femoral Nerve | Anterior/lateral femoral shaft → Patella | Extends knee |
Note: The iliotibial tract is a thickened band of fascia lata extending from the iliac crest to the lateral knee.

Gluteal Muscles
| Muscle | Nerve Supply | Origin → Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gluteus Maximus | Inferior Gluteal | Ilium, sacrum, coccyx → Gluteal tuberosity & iliotibial tract | Extends, laterally rotates, abducts thigh |
| Gluteus Medius | Superior Gluteal | Ilium (between ant/post gluteal lines) → Greater trochanter | Abducts, medially rotates thigh; stabilises pelvis during gait |
| Gluteus Minimus | Superior Gluteal | Ilium (between ant/inf gluteal lines) → Greater trochanter | Abducts, medially rotates thigh; stabilises pelvis during gait |
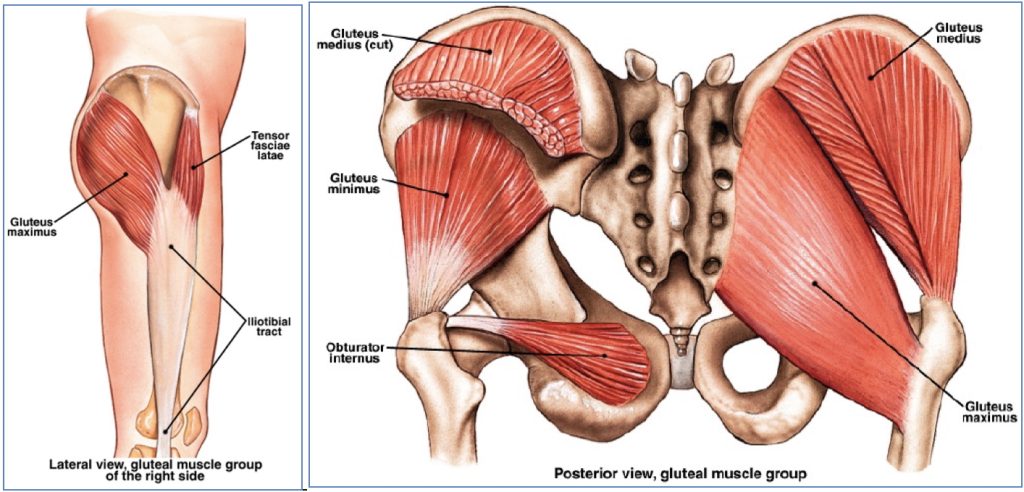

Lateral Rotators of the Hip
| Muscle | Nerve Supply | Origin → Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piriformis | S1, S2, L5 | Anterior sacrum → Superior greater trochanter | Lateral rotation, adduction; stabilises hip |
| Gemellus Superior | L5, S1 | Ischial spine → Greater trochanter | Same as above |
| Obturator Internus | L5, S1 | Obturator membrane (inner) → Greater trochanter | Same as above |
| Gemellus Inferior | L5, S1 | Ischial tuberosity → Greater trochanter | Same as above |
| Obturator Externus | Obturator Nerve | Obturator membrane (outer) → Trochanteric fossa | Same as above |
| Quadratus Femoris | L5, S1 | Ischial tuberosity → Trochanteric crest of femur | Lateral rotation; stabilises hip |
Thigh Muscles – Posterior Compartment
| Muscle | Nerve Supply | Origin → Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biceps Femoris | Long: Sciatic-Tibial Short: Common Fibular | Ischial tuberosity (long), linea aspera (short) → Head of fibula & lat. tibial condyle | Extends thigh; flexes/laterally rotates flexed knee |
| Semitendinosus | Sciatic-Tibial Nerve | Ischial tuberosity → Medial tibial shaft | Extends thigh; flexes/medially rotates knee |
| Semimembranosus | Sciatic-Tibial Nerve | Ischial tuberosity → Medial tibial condyle | Same as above |

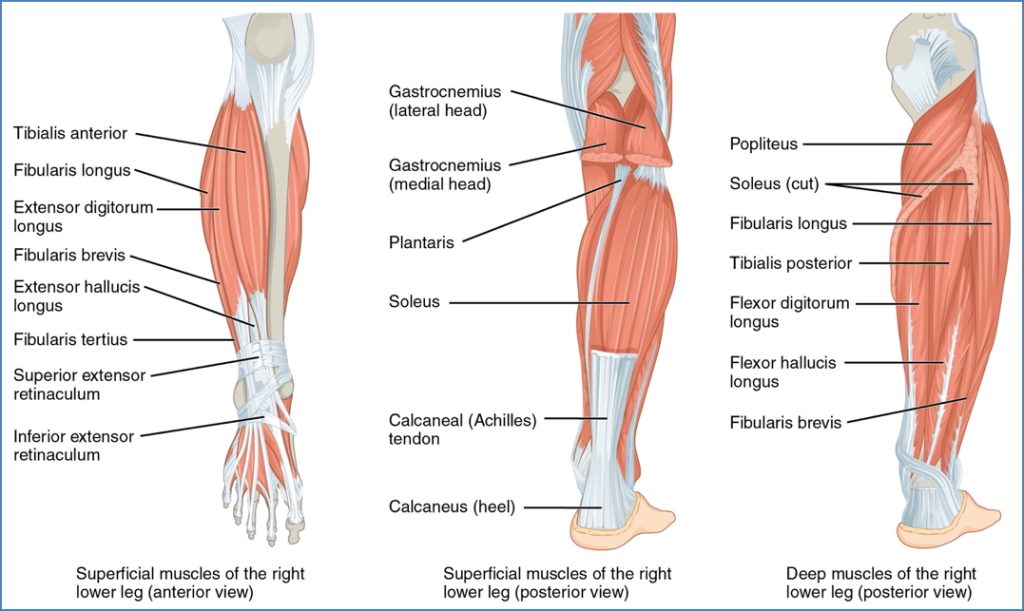
Anterior Compartment of Leg
| Muscle | Nerve Supply | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Tibialis Anterior | Deep Fibular | Dorsiflexion |
| Extensor Hallucis Longus | Deep Fibular | Extension of great toe |
| Extensor Digitorum Longus | Deep Fibular | Extension of digits 2–5 |
| Fibularis Tertius | Deep Fibular | Dorsiflexion |
Lateral Compartment of Leg
| Muscle | Action |
|---|---|
| Fibularis Longus | Eversion, plantarflexion |
| Fibularis Brevis | Eversion, plantarflexion |
Posterior Compartment of Leg
| Muscle | Action |
|---|---|
| Gastrocnemius (med & lat) | Plantarflexion, knee flexion |
| Soleus | Plantarflexion |
| Plantaris | Weak plantarflexion |
| Tibialis Posterior | Plantarflexion, arch support |
| Flexor Digitorum Longus | Flexes digits 2–5 |
| Flexor Hallucis Longus | Flexes great toe |

Intrinsic Muscles of the Foot
Plantar Aspect
Layer 1:
- Abductor Hallucis
- Flexor Digitorum Brevis
- Abductor Digiti Minimi
Layer 2:
- Quadratus Plantae
- Lumbricals
- Flexor Hallucis Brevis
- Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis
Layer 3:
- Adductor Hallucis (Oblique & Transverse Heads)
Layer 4:
- Plantar Interossei – Adduct toes
Dorsal Aspect
Layer 1:
- Extensor Hallucis Brevis
- Extensor Digitorum Brevis
Layer 2:
- Dorsal Interossei – Abduct toes


Key Anatomical Regions
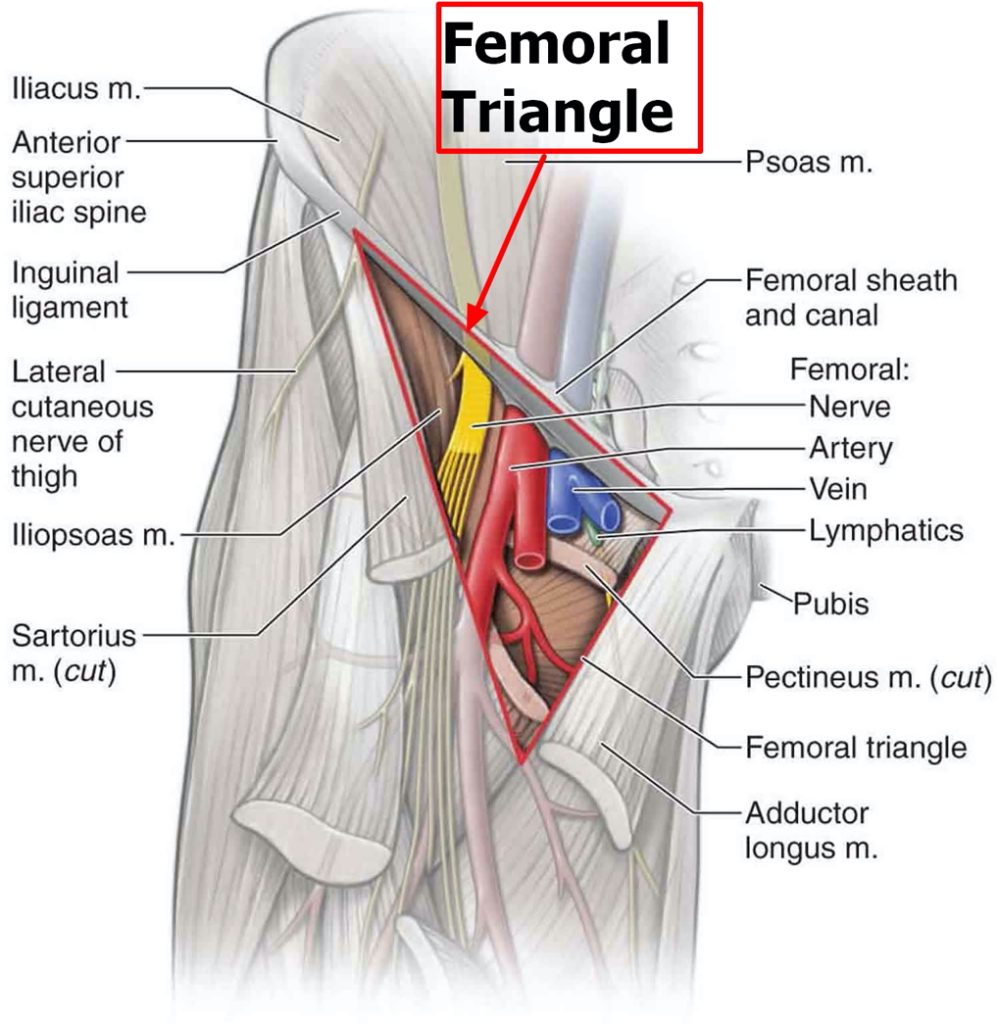
Femoral Triangle
Boundaries:
- Superior: Inguinal Ligament
- Lateral: Sartorius
- Medial: Adductor Longus
Corners:
- Inferior: Sartorius meets Adductor Longus
- Superior: Sartorius meets Inguinal Ligament
- Medial: Adductor Longus meets Pectineus
Contents *(Remember: NAVEL)*:
- Femoral Nerve
- Femoral Artery
- Femoral Vein
- Empty space
- Inguinal Lymphatics

Popliteal Fossa
- Diamond-shaped region behind the knee
- Boundaries:
- Superomedial: Semimembranosus & Semitendinosus
- Superolateral: Biceps femoris
- Inferomedial/lateral: Gastrocnemius (medial & lateral heads)
Contents:
- Popliteal artery & vein
- Tibial nerve
- Common fibular nerve


Malleolar Structures
Medial Malleolus:
Mnemonic: Tom, Dick, And Nervous Harry
- Tibialis Posterior
- Flexor Digitorum Longus
- Posterior Tibial Artery
- Tibial Nerve
- Flexor Hallucis Longus


Lateral Malleolus:
- Fibularis Longus
- Fibularis Brevis


Summary – Lower Limb Muscles
The lower limb muscles are organised anatomically and functionally to allow complex and powerful movements. From pelvic stabilisation to precise toe control, these muscles play essential roles in gait, posture, and athletic performance. Familiarity with their origins, insertions, and actions is crucial for clinical practice. For a broader context, see our Musculoskeletal Overview page.