Table of Contents
Overview
Osteomyelitis is a serious infection of the bone, most commonly caused by bacterial pathogens. It can occur via hematogenous spread, direct inoculation (e.g. trauma, surgery), or contiguous spread from nearby infected tissue. Prompt recognition and treatment are essential to avoid chronic infection, necrosis, or limb loss.
Definition
Osteomyelitis refers to infection and inflammation of bone tissue, typically involving the medullary cavity, cortex, and periosteum.
Aetiology
| Type | Common Pathogens |
|---|---|
| Bacterial | Staphylococcus aureus (most common) |
| Iatrogenic | Pseudomonas aeruginosa (post-surgical) |
| Paediatric cases | Haemophilus influenzae |
| Others | Viral, fungal (immunocompromised patients) |
Pathogenesis
- Infection usually initiates in the medullary cavity, spreading to cortical bone and then to the periosteum
- This leads to inflammation, oedema, and ischemic necrosis of bone tissue
- Chronic infection may result in sequestra (dead bone) and involucrum (new bone formation around dead tissue)
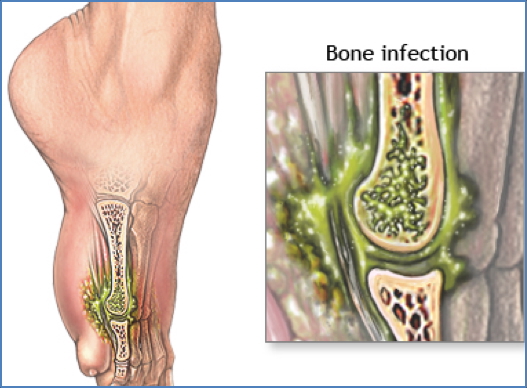
Morphology
- Macroscopic: Localised swelling, erythema, and heat
- Microscopic: Suppurative medullary inflammation, vascular congestion, and neutrophilic infiltration
Clinical Features
- History of:
- Recent infection elsewhere (e.g. skin, urinary tract)
- Direct trauma or surgery to affected area
- Local signs:
- Tenderness, swelling, erythema, warmth, reduced ROM near metaphysis
- Systemic signs of acute sepsis:
- Fever, chills, lethargy, dehydration
Investigations
| Modality | Findings |
|---|---|
| Blood Tests | ↑ WBC, ↑ ESR, ↑ CRP, positive blood cultures |
| X-ray | Normal in acute phase; lucencies after 2–4 weeks; “onion-skin” appearance if chronic |
| MRI/CT | Medullary oedema, cortical destruction, joint involvement |

Treatment
Medical
- Long-term IV antibiotics (4–6 weeks)
- Options include:
- Vancomycin
- Rifampicin
- Erythromycin
- Tetracycline
- Options include:
Surgical
- Irrigation and debridement
- Amputation (if severe necrosis or chronic refractory infection)
- Replacement of infected prosthetic devices
Summary – Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is a potentially limb-threatening bone infection. It requires a high index of suspicion, especially in patients with recent infections, open fractures, or prostheses. Diagnosis relies on blood tests and imaging, with treatment involving prolonged antibiotics and possibly surgery. For a broader understanding of musculoskeletal infections and bone conditions, visit our Musculoskeletal Overview page.