Table of Contents
Overview – Appendicitis
Appendicitis is one of the most common causes of acute abdominal pain requiring surgical intervention. It typically results from obstruction of the appendiceal lumen, often due to a faecolith, which leads to inflammation, bacterial overgrowth, and potentially life-threatening complications like perforation and sepsis. Timely diagnosis is critical, as early intervention via appendectomy dramatically improves outcomes. Final-year medical students must be confident in recognising its classical signs and knowing when urgent surgical referral is needed.
Definition
- Inflammation of the vermiform appendix, typically due to luminal obstruction.
Aetiology
- Idiopathic in most cases
- Most common underlying factor: faecolith obstruction
Pathophysiology
- Obstruction (usually by faecolith) → stasis of luminal contents
→ bacterial overgrowth → inflammation → ischaemia → gangrene → possible perforation and peritonitis
Morphology
- Enlarged, thickened, inflamed appendix
- May become necrotic or perforated if not treated
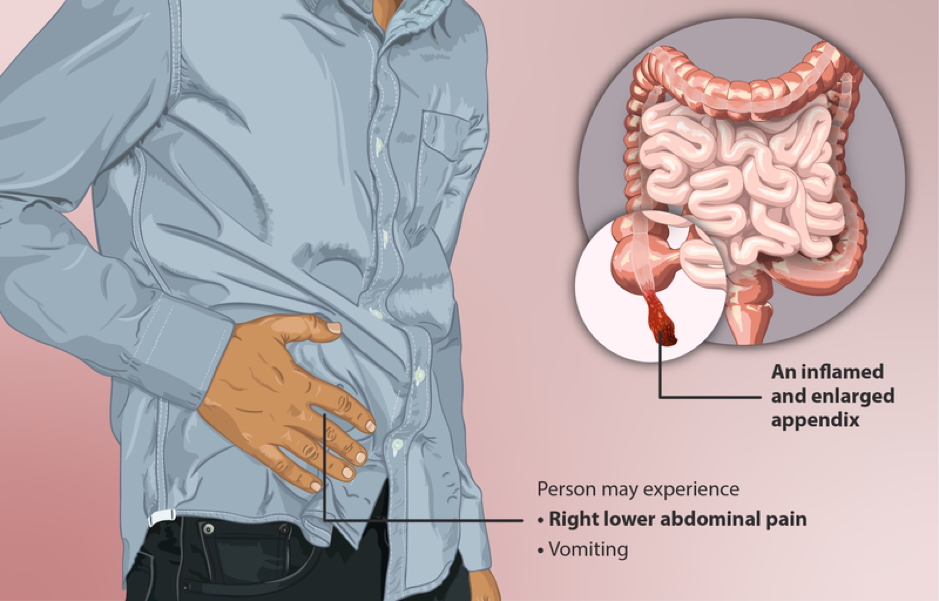
Clinical Features
- Pain Pattern:
- Initially vague, peri-umbilical pain, localising to right iliac fossa (RIF) within 12–24 hrs
- GI Symptoms:
- Nausea, vomiting, anorexia
- Occasional diarrhoea
- RIF Signs:
- Tenderness, guarding, rebound tenderness
- Rovsing’s sign: pain in RIF on palpation of LIF
- Psoas sign: pain on extension/flexion/internal rotation of hip
- McBurney’s sign: tenderness at McBurney’s point
- Obturator sign: pain with internal rotation of flexed thigh
- Referred rebound tenderness in LIF

Investigations
- Bloods:
- ↑WBC (neutrophilia)
- ↑ESR, ↑CRP
- Imaging:
- Ultrasound or CT – confirms thickened, inflamed appendix
- CT preferred for diagnostic accuracy in atypical cases
Management
- Stabilisation:
- IV fluids
- Group and hold (for potential transfusion)
- Antibiotics (Pre-op Prophylaxis):
- Ampicillin + Gentamicin + Metronidazole
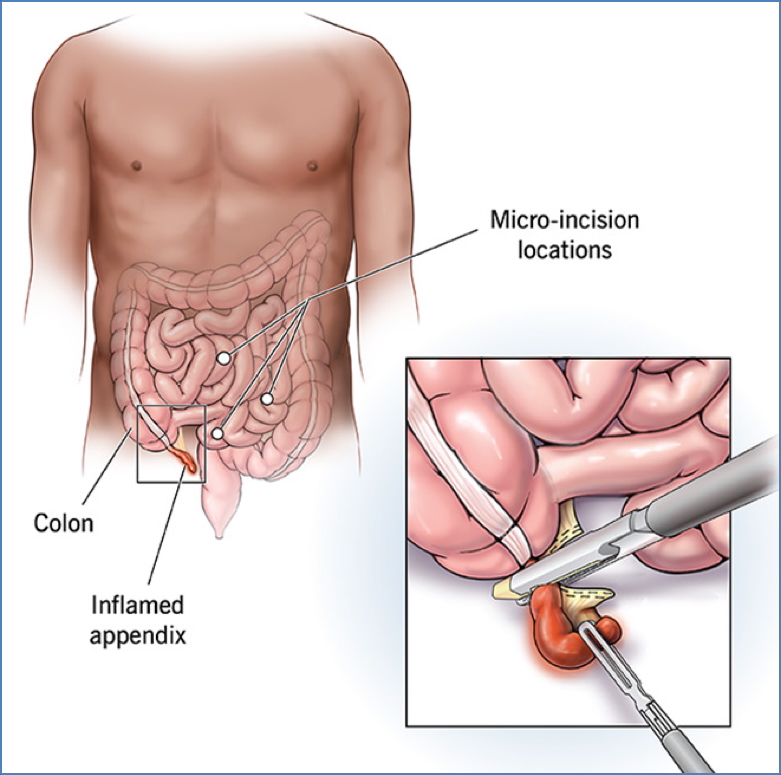
- Definitive Treatment:
- Appendectomy – laparoscopic preferred unless contraindicated

Complications
- Perforation
- Sepsis and peritonitis
- Abscess formation if localised perforation
- Post-operative wound infection or adhesions
Summary – Appendicitis
Appendicitis is a common surgical emergency caused by luminal obstruction and subsequent inflammation of the appendix. Classical progression from peri-umbilical pain to RIF tenderness, along with supportive labs and imaging, guides the diagnosis. Prompt treatment with antibiotics and appendectomy prevents serious complications like perforation and sepsis. For related topics, visit our Gastrointestinal Overview page.