Table of Contents
Overview – Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is a central neuroendocrine organ that serves as a critical interface between the nervous and endocrine systems. Located beneath the thalamus, it integrates information from various brain regions to regulate numerous homeostatic processes, including temperature, hunger, and hormonal balance. Understanding the hypothalamus is essential for appreciating its role in both health and disease, particularly within the field of endocrinology.
Location
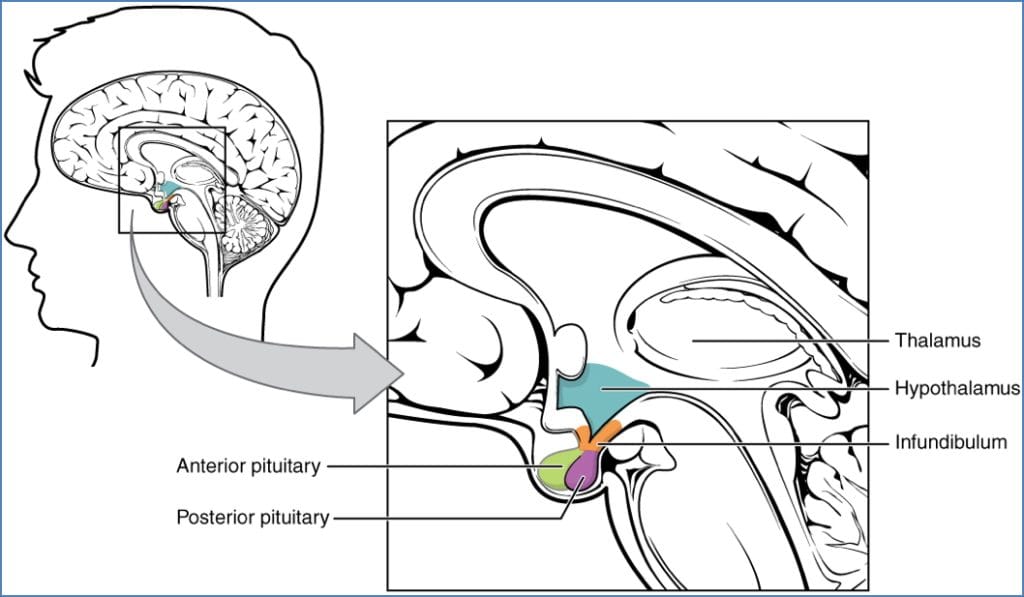
- The hypothalamus is located in the diencephalon, at the base of the brain just below the thalamus.
- “Hypo”-thalamus literally means “below the thalamus”.
- It links the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, orchestrating hormonal responses based on neural inputs.

Functions
- Integrates information from multiple higher brain centres.
- Determines appropriate physiological responses and signals the pituitary gland to release or inhibit hormone secretion.
- Regulates:
- Body temperature
- Hunger and satiety
- Thirst
- Fatigue and sleep cycles
- Emotional responses (anger, fear)
- Circadian rhythms
- Synthesises and secretes neurohormones (hypothalamic-releasing hormones) that modulate pituitary activity.
Inputs to the Hypothalamus
- Reticular Activating System (RAS): Regulates drowsiness via serotonin release.
- Thalamus: Involved in pain perception.
- Neocortex & Limbic System: Process emotions such as fear, rage, and pleasure.
- Optical System: Integrates visual information for circadian rhythm regulation.


Outputs from the Hypothalamus
- Anterior Pituitary: Via releasing and inhibiting hormones.
- Posterior Pituitary: Direct neural control for hormone secretion.
- Brain Stem: Autonomic nervous system regulation (e.g. cardiovascular, thermoregulation).
Hypothalamic Regulatory Hormones
| Abbreviation | Full Name | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| GHRH | Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone | Stimulates GH release |
| SS | Somatostatin | Inhibits GH & TSH release |
| TRH | Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone | Stimulates TSH & prolactin release |
| PRH | Prolactin-Releasing Hormone | Stimulates prolactin release |
| GnRH | Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone | Stimulates FSH & LH release |
| CRH | Corticotrophin-Releasing Hormone | Stimulates ACTH release |
| PIH | Prolactin-Inhibiting Hormone (Dopamine) | Inhibits prolactin release |


Summary – Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus plays a vital role in homeostasis, linking the nervous and endocrine systems through its regulation of the pituitary gland. Its diverse inputs and regulatory hormones enable precise control over numerous physiological functions. For a broader context, see our Endocrine Overview page.